
Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): Hip Impingement
Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) is a condition where the hip joint is not shaped normally. Also known as hip impingement, it causes the bones to rub together causing pain, and can be treated with corticosteroids, NSAIDs, physical therapy, rest, and sometimes hip surgery is required.
What is Femoroacetabular Impingement?
FAI describes when a hip joint is shaped incorrectly, allowing two bones in the hip to rub together causing friction between the femur (thighbone) and acetabulum (a part of the pelvis). Femoroacetabular Impingement, or hip impingement, can limit motion and be a painful condition that without treatment can damage the cartilage which provides cushion in the hip.
Hip Impingement Symptoms & Causes
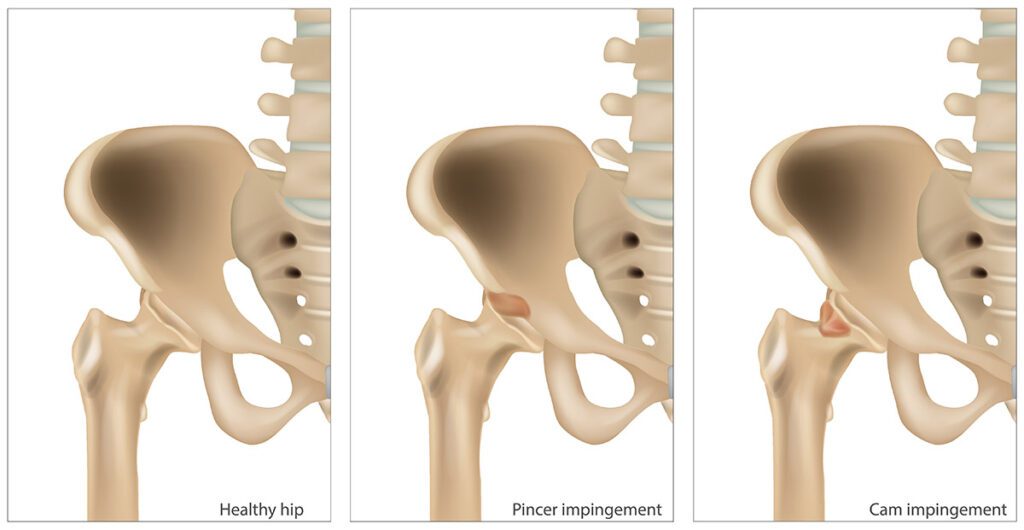
FAI abnormalities are usually present at birth but can develop later in life, often in the teenage years and among athletes of all ages. Whether a person was born with FAI or it developed later, it is categorized into three types based on the direct cause:
- Cam: FAI that occurs due to a bony growth on the head of the femur, sometimes caused by physical activity.
- Pincer: Caused by extra bone growth in the hip socket, usually during a child’s development.
- Combined: Both the cam and pincer FAI types are present
It’s important to note that not all people with FAI experience symptoms, but signs can appear as the damage in the hip progresses and worsens:
- Hip pain, which worsens during physical activity or long periods of sitting
- Limping
- Hip stiffness
Femoroacetabular Impingement Diagnosis & Tests
There are several tests to help diagnose FAI, including:
- Imaging tests, such as MRIs or X-rays to see signs of damage and identify any abnormalities in the hip joint.
- Local anesthetic to test whether numbing the hip joint relieves pain or not.
- Impingement test: A doctor brings the knee up to the chest and rotates it toward the opposite shoulder. If a patient has FAI, they will feel the same kind of pain with the movement.
- Physical exam to determine the range of motion, muscle strength, and the way the patient walks to see if the hip joint is working properly.
Hip Impingement Treatments
Treating hip impingement depends on the severity of the damage and the person’s needs but generally includes:
- Corticosteroids: drugs that help reduce inflammation in and around the hip joint, often administered via injection
- Physical therapy: exercises to help strengthen the joint and improve mobility
- NSAIDs/Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: medicines that reduce inflammation and typically given in pill form.
- Rest: limiting activity that causes friction in the hip joint.
Hip Surgery
In some cases, FAI requires hip surgery, with two choices depending on the needs of the patient:
- Arthroscopic hip surgery: a minimally invasive procedure where a doctor removes or repairs damaged bone or cartilage using an arthroscope.
- Traditional hip surgery: used in more severe cases of FAI, a surgeon will make a larger incision to repair damage to the hip joint without the use of smaller tools (as is with an arthroscope).